联系我们
核心技术
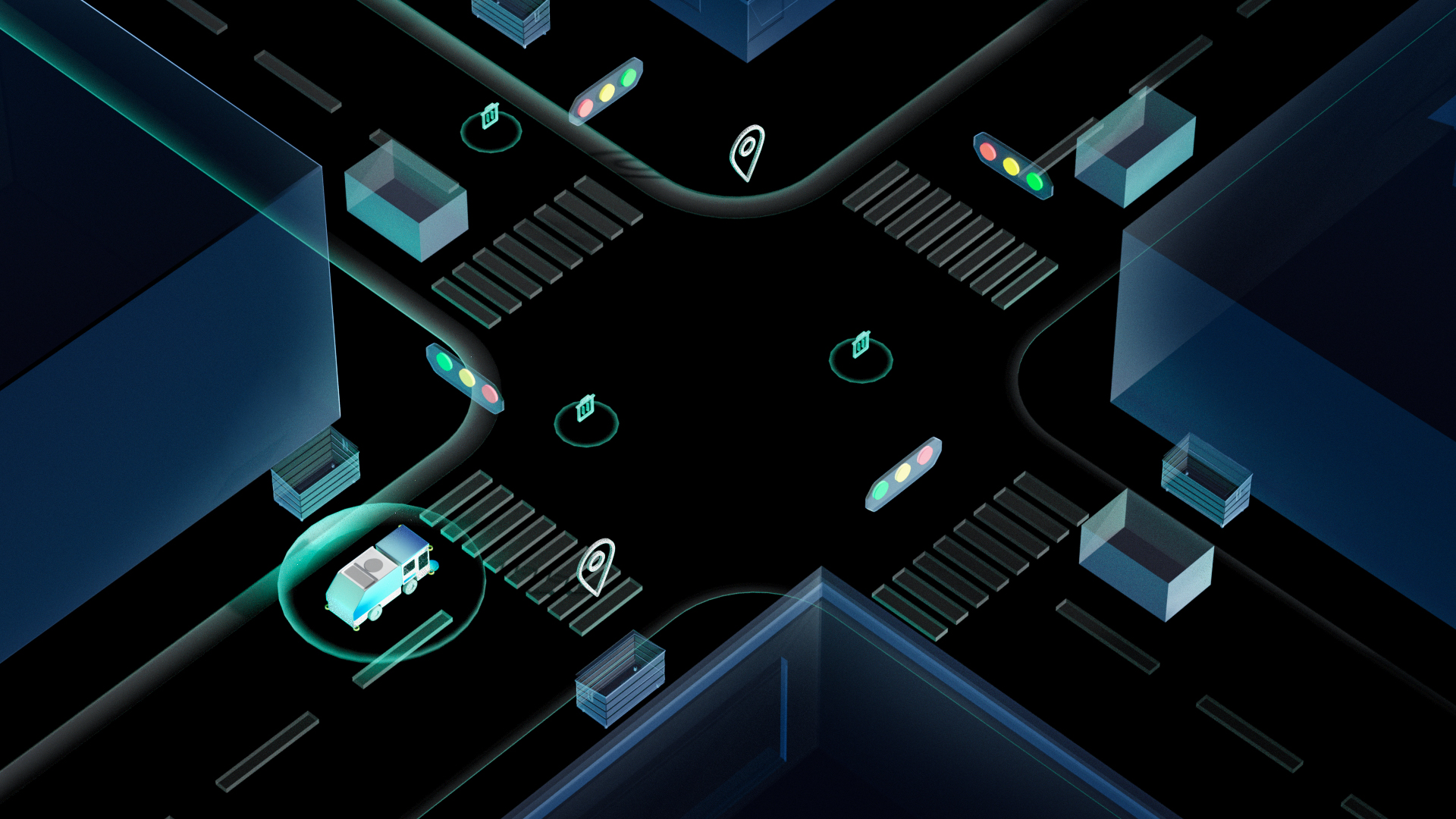

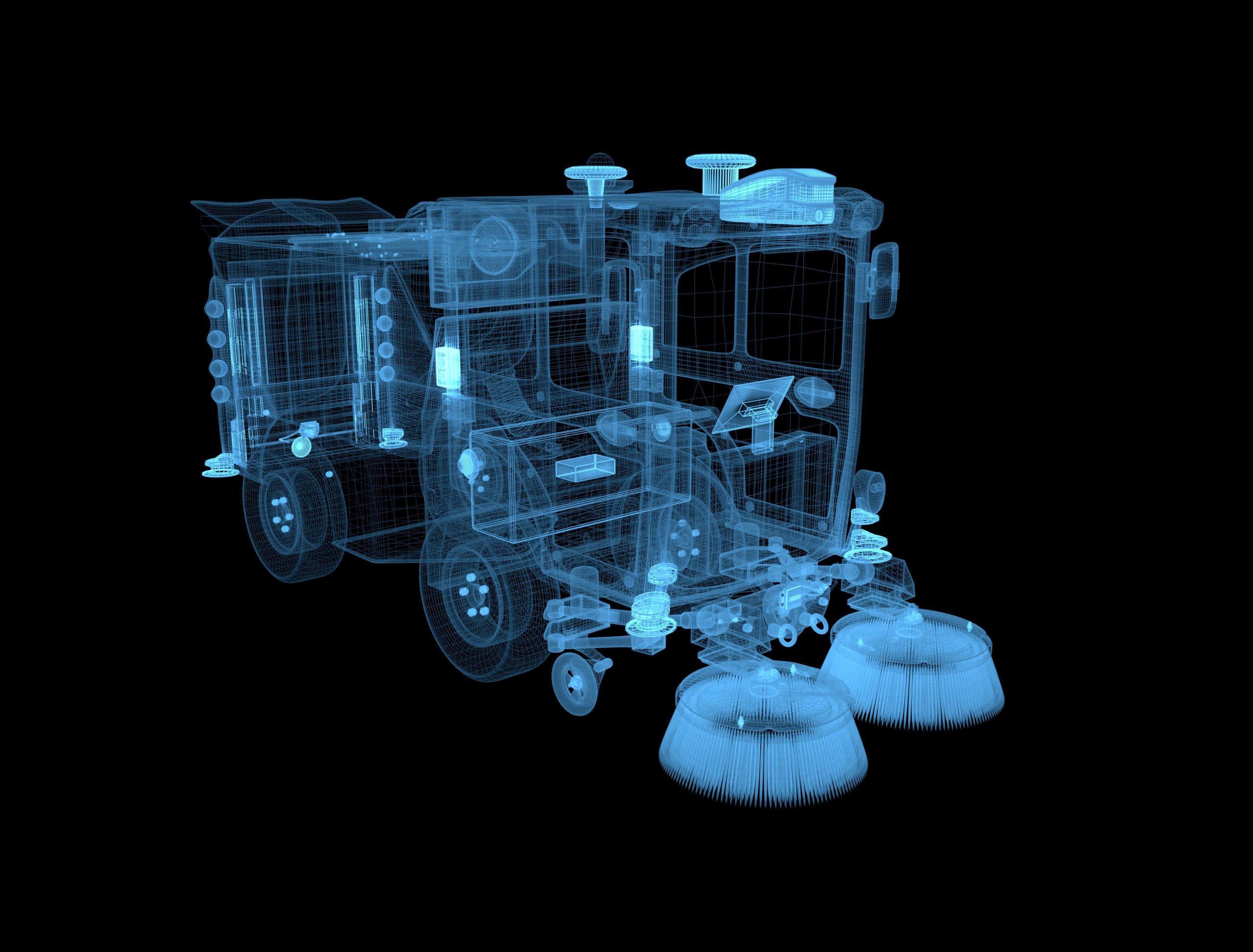
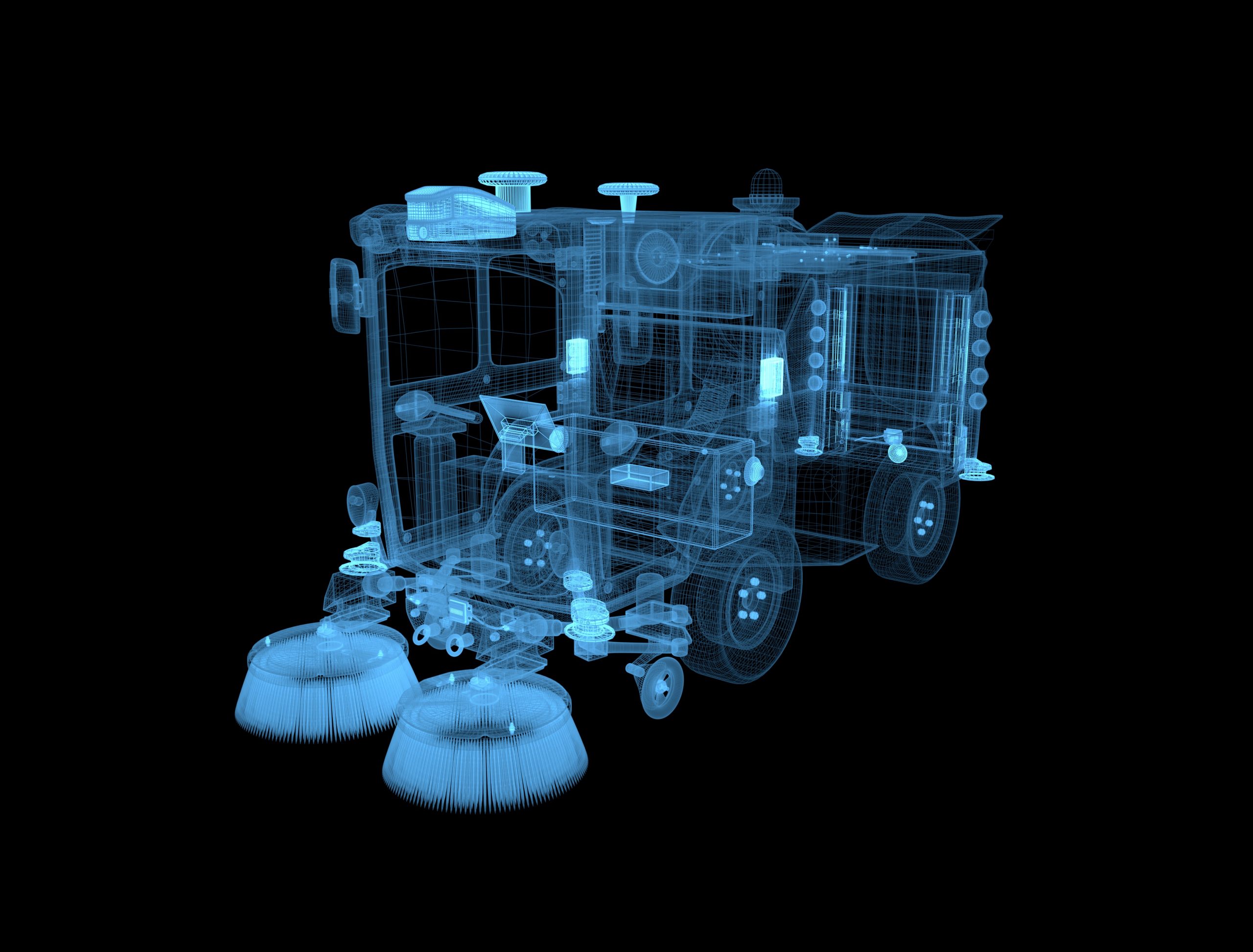
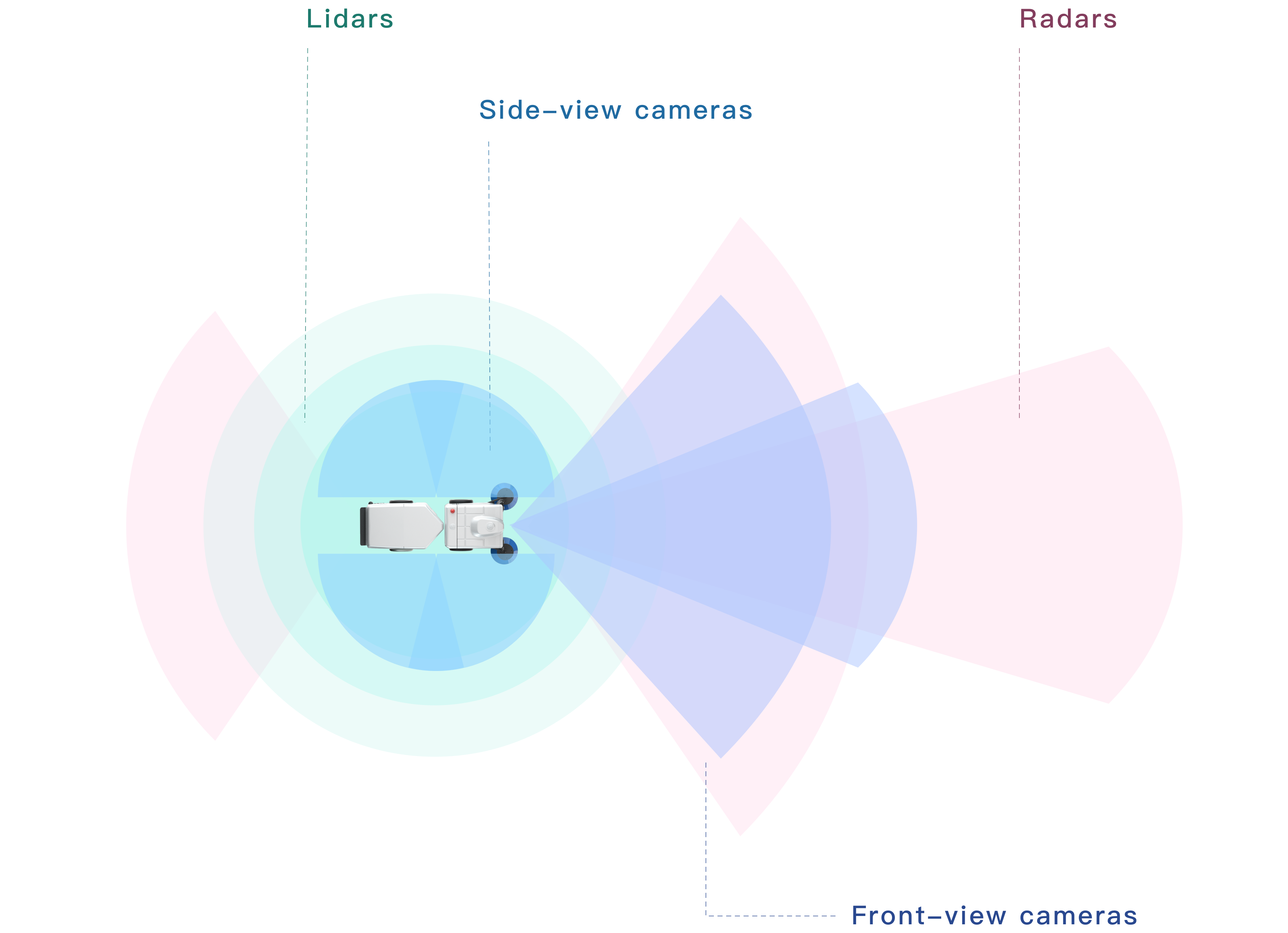
感知模块
基于多传感器的传统算法+BEV的多层冗余方案,以一个多任务大模型支持常见的交通参与元素与长尾通用障碍物的检测识别,提升可靠性和安全性。
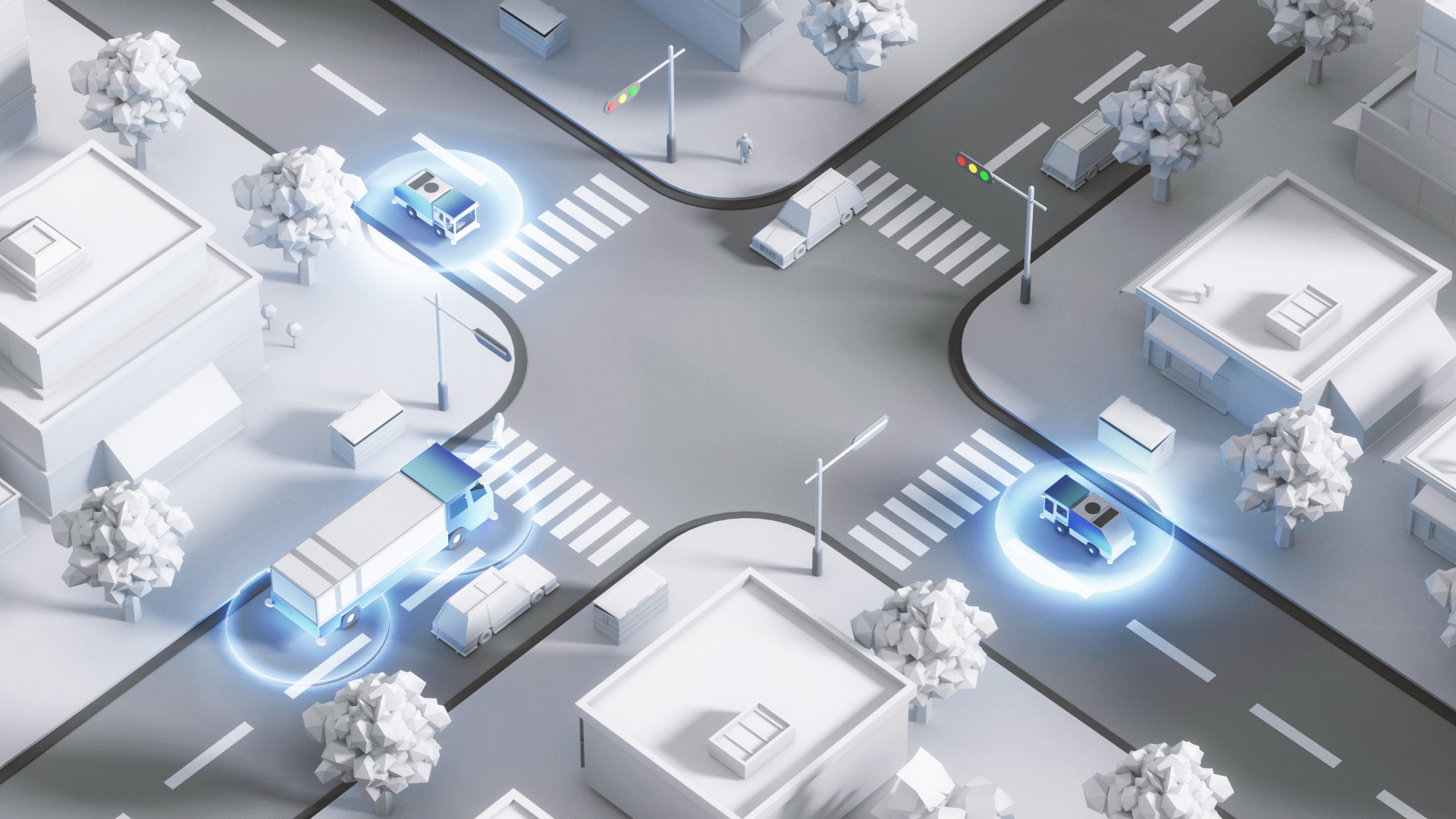

定位模块
基于高精地图和现场实时定位,实现厘米级定位,误差3cm以内,确保贴边清扫。
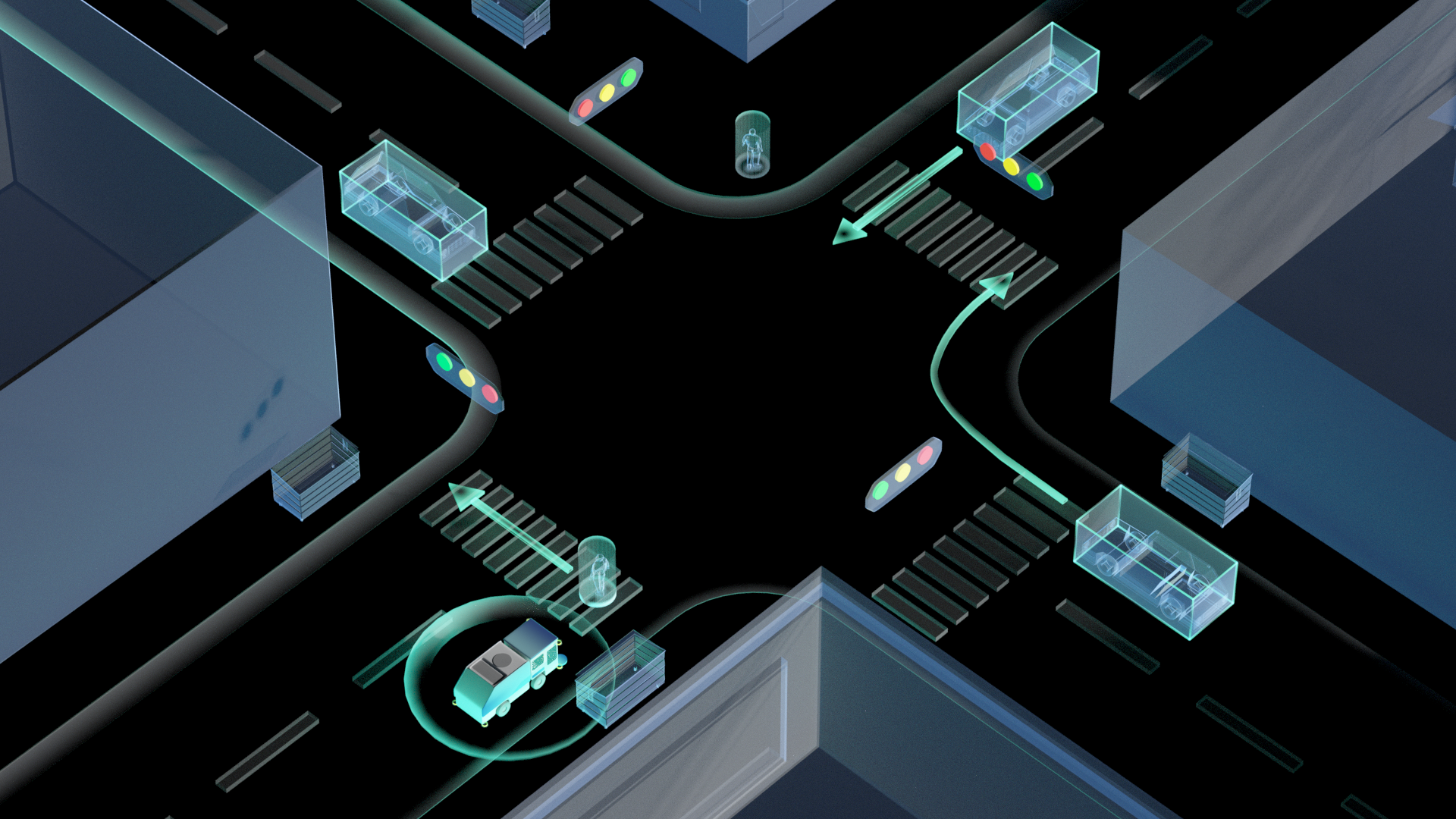
预测模块
对100+障碍物在10ms内能完成同时预测,预测结果与Waymo motion prediction 第一名的 3s 指标持平。
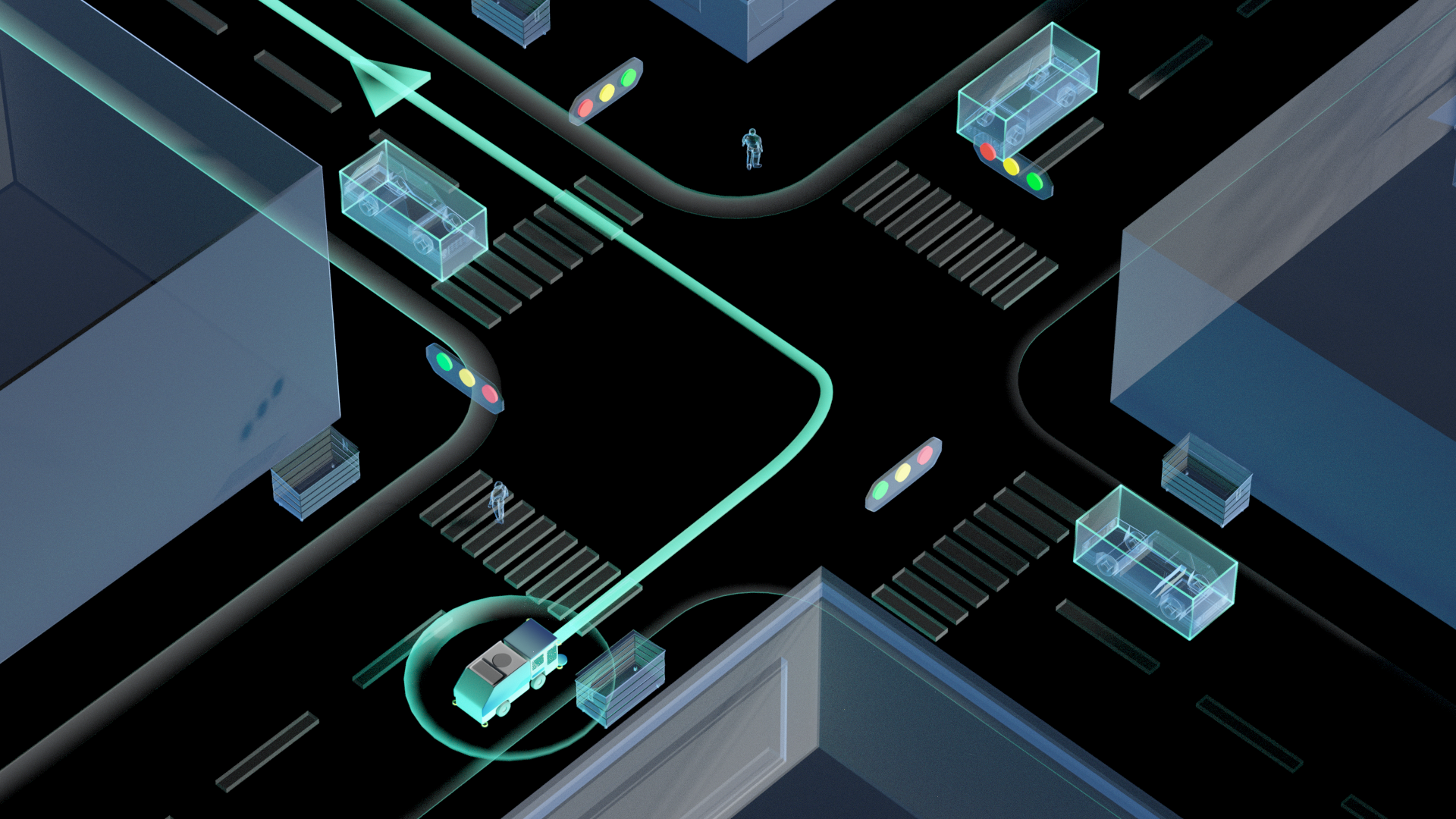
规划模块
采用3D规划,基于欧式坐标系无膨胀的精细化贴边轨迹,考虑自车3D形体(扫刷、车体突出传感器等)和不同高度、材质的路边障碍物交互。
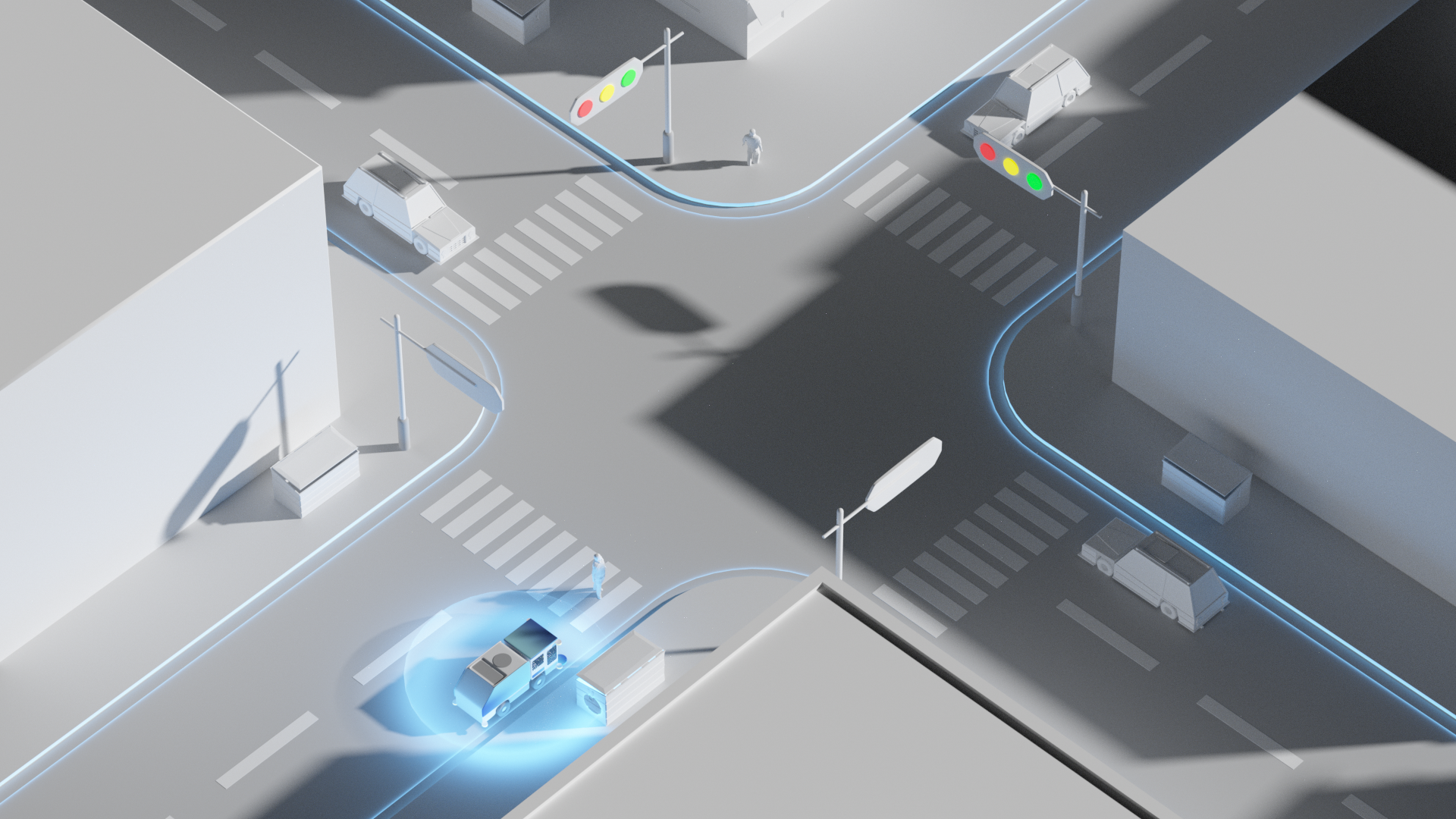
控制模块
使用车规级线控制动系统和双备转向系统,响应精度高。

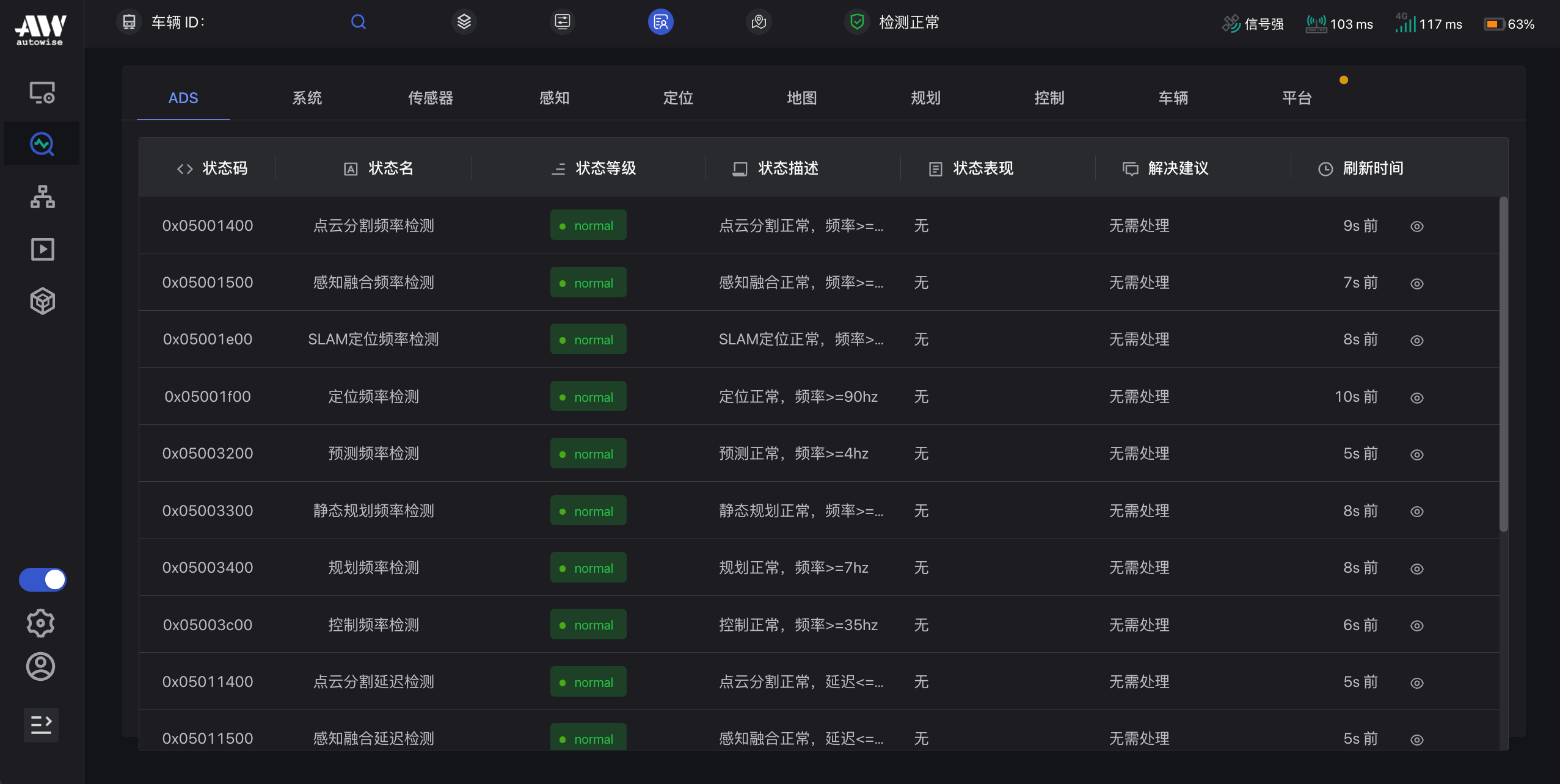
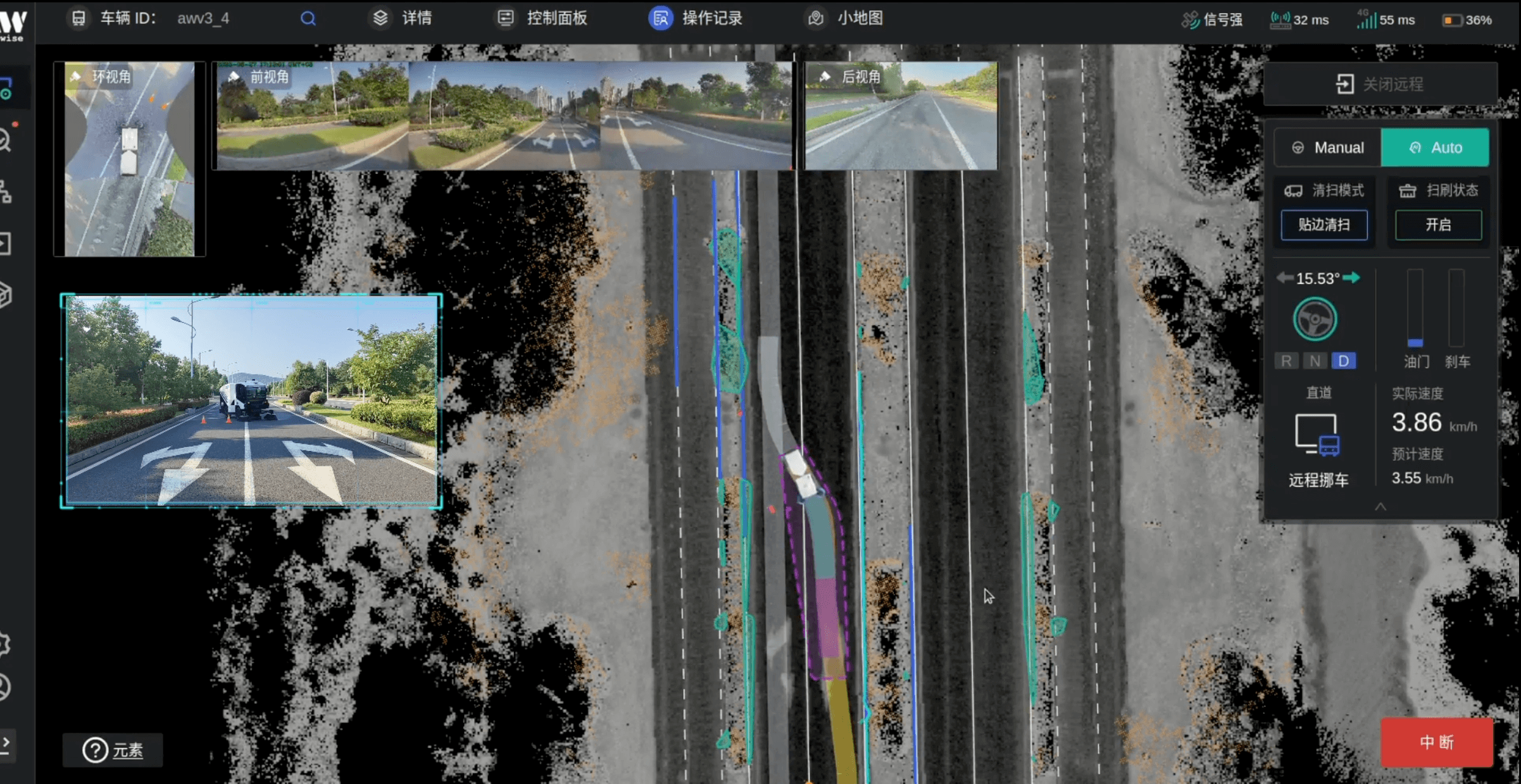
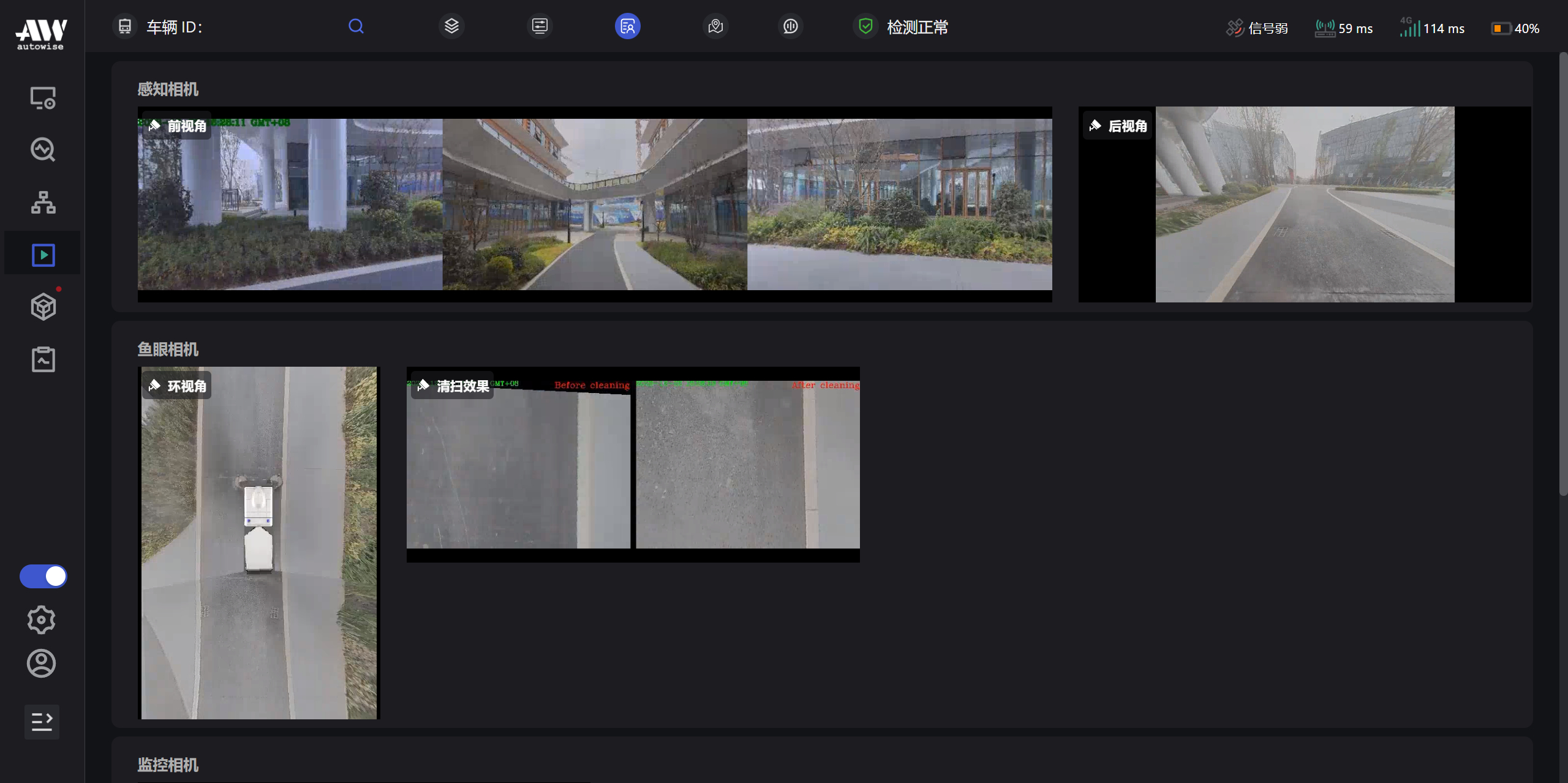
远程运营平台 Radar24
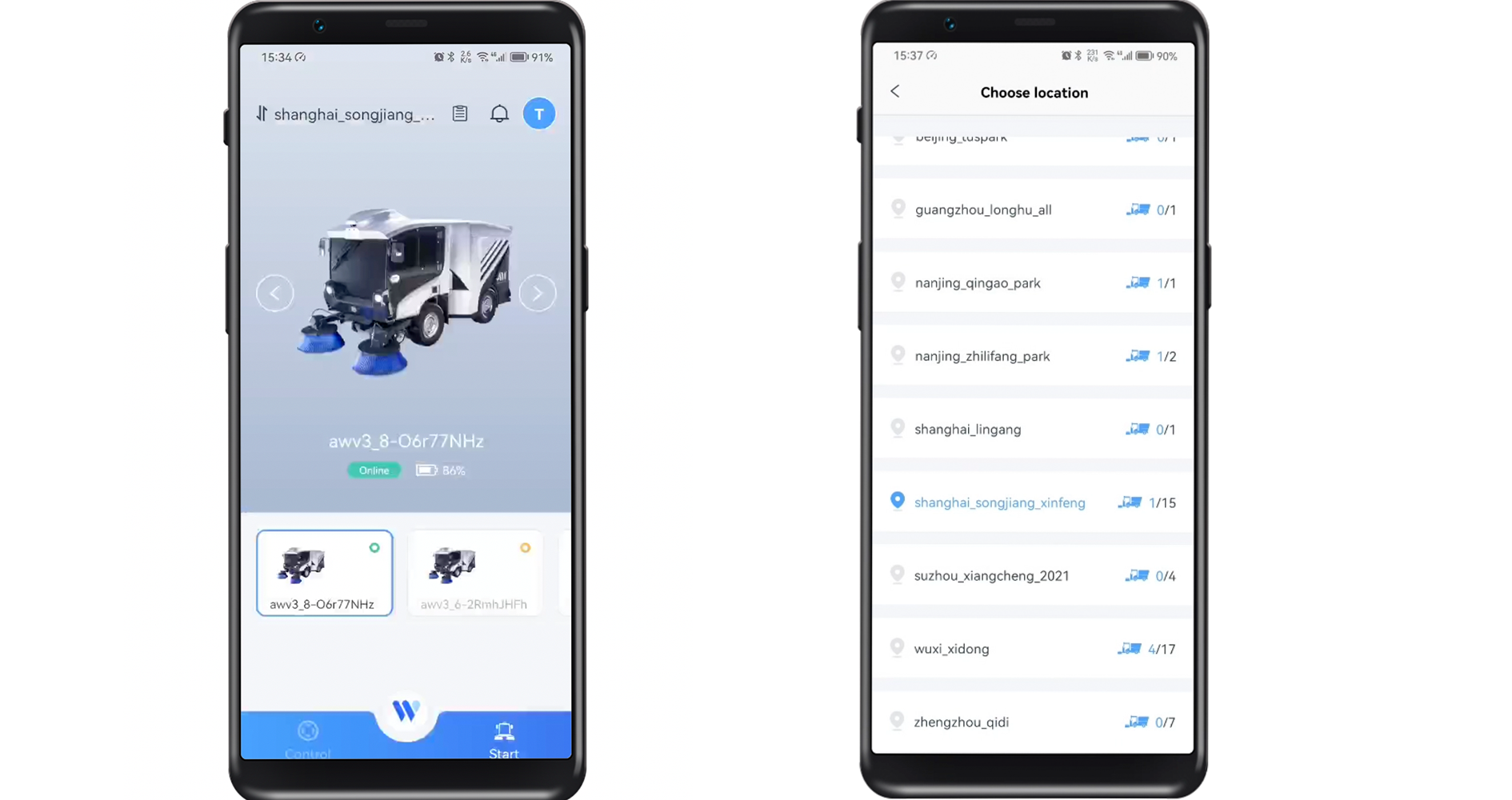
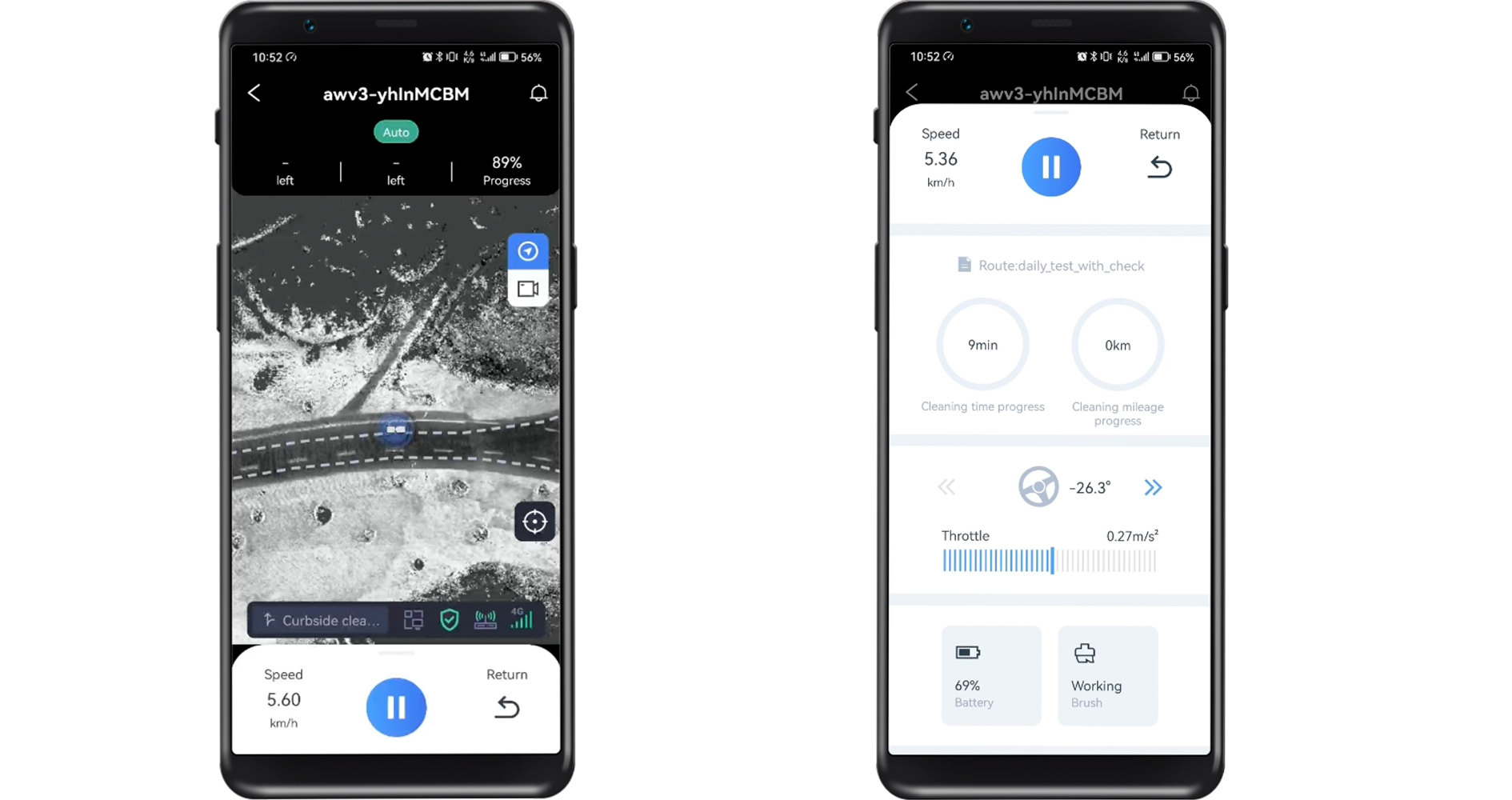
远程运营APP WiAction

自动紧急制动系统 (AEB)
使用传感器探测自动驾驶清扫车与物体、行人和周围车辆的距离,在碰撞可能发生时,采取紧急制动。在手动模式下,如果系统判定即将发生碰撞,AEB也会发出预警。

交通信号灯识别
在集成算法和车载摄像头的辅助下,自动驾驶清扫车能够识别交通信号灯,遇红灯时停止,遇绿灯时行驶。
物体检测
自动驾驶清扫车使用传感器识别附近的人类、动物、静止物体或移动物体。如果遇到障碍物,清扫车会自动调整路线,避免碰撞。












FOLLOW US